Circulation pumps are small devices that quietly influence the comfort, efficiency, and reliability of homes and commercial buildings. While they are not the most visible part of a heating or hot-water system, they are one of the most important. A well-chosen circulation pump ensures steady temperatures, faster access to hot water, and lower energy costs. With more options available from different brands, including general-purpose models from companies such as BritTherm, it has become easier for buyers to find pumps that suit their systems. This guide explains circulation pumps in a clear, helpful way so readers can make informed decisions.
What Exactly Is a Circulation Pump?
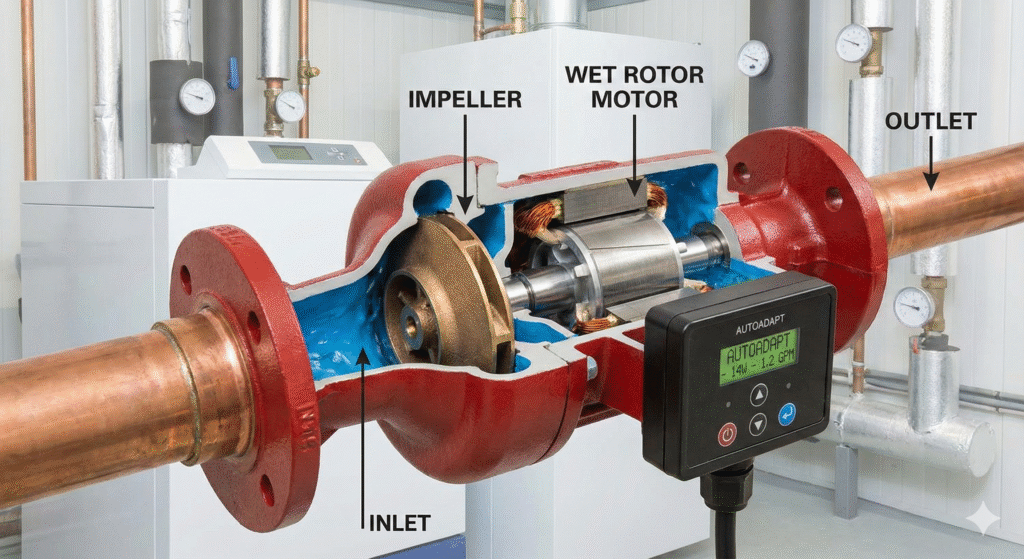
A circulation pump is a compact device designed to move water through a closed-loop system. Unlike pumps that push water from one location to another, circulation pumps keep the same water moving continuously. This makes them ideal for:
Central heating systems
Underfloor heating
Domestic hot-water recirculation
Cooling systems
Small industrial processes
In a heating system, the pump carries heated water from the boiler to radiators or underfloor pipes, ensuring even temperature distribution. In a hot-water supply line, it reduces the wait time for warm water at taps. In cooling systems, it moves chilled water to maintain stable temperatures.
Because circulation pumps operate in loops, they don’t require the same lifting power as deep-well pumps. This allows them to be small, efficient, and quiet.
Why Circulation Pumps Matter in Modern Buildings
Many homeowners only pay attention to circulation pumps when something stops working—cold radiators, strange noises, or long delays before hot water arrives. But when functioning correctly, these pumps provide several key advantages.
1. Stable Indoor Temperatures
A good circulation pump keeps water flowing at a constant rate. This reduces cold spots in heating systems and keeps floors warm in underfloor heating setups.
2. Energy Savings
Modern circulation pumps use significantly less electricity than older models. Some operate with variable-speed motors that adjust automatically to system demand. Pumps found on platforms like www.brittherm.co.uk often fall into this newer category, reflecting industry trends toward improved efficiency.
3. Longer System Life
Circulation pumps help prevent blockages, freezing, sediment buildup, and corrosion. Consistent movement of water reduces stress on pipes, boilers, and radiators.
4. Better Overall Comfort
Shorter waiting times for hot water can save both energy and water. Buildings become more comfortable and efficient because temperature changes happen more smoothly.
Common Types of Circulation Pumps
Different systems require different pump designs. The most common types include:
● Single-Speed Pumps
These older pumps operate at one constant speed. They are simple and reliable but not very energy-efficient by modern standards.
● Multi-Speed Pumps
Offering two or three speed settings, these pumps let installers adjust flow rates manually. They work well in systems with predictable demand.
● Variable-Speed (High-Efficiency) Pumps
These pumps automatically adapt their speed to real-time system requirements. They are quieter, use less electricity, and produce minimal vibrations. Many new installations prefer these pumps for their long-term savings.
● Hot-Water Recirculating Pumps
These are designed specifically to move warm water through domestic supply lines so that faucets deliver hot water immediately.
● Inline and Flange Pumps
The connection type varies depending on pipe layout. Inline pumps are common in smaller systems, while flange pumps fit larger installations.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Circulation Pump
Choosing the right pump does not simply mean picking the most powerful model. A pump must match the needs of the system. Below are important factors buyers should consider:
1. Flow Rate (Litres per Minute or Hour)
This determines how much water can move through the system. Too low a flow rate leads to cold spots; too high can cause noise and wear.
2. Head Pressure
Head pressure measures how far the pump can push water through pipes and bends. Buildings with long pipe runs or multiple floors may require a pump with higher head capacity.
3. Energy Consumption
Energy efficiency matters for long-term cost savings. High-efficiency pumps reduce electricity use significantly.
4. Noise Levels
Quieter pumps are essential for homes, especially when installed near bedrooms or living areas.
5. Installation Compatibility
Pipe connections, pump size, and power requirements must match the system. This is why checking technical data—such as those available from BritTherm—can be helpful before purchasing.
6. Material and Durability
Stainless steel and brass components resist corrosion. Durable motors extend lifespan and reduce maintenance needs.
Warning Signs That a Circulation Pump Needs Maintenance
Circulation pumps last several years, but problems can appear gradually. Homeowners should pay attention to:
Radiators not heating evenly
Sudden increases in energy bills
Loud humming, rattling, or grinding noises
Water taking longer to heat
Vibrations in pipes
Pump housing feeling unusually hot
Sometimes the issue is simple, such as trapped air or low system pressure. Other times, the pump may be approaching the end of its life.
Typical Causes of Pump Failure
When circulation pumps fail, the causes often include:
● Wear and Tear
Continuous operation eventually weakens internal components.
● Sediment or Scale
Mineral buildup restricts water flow and forces the pump to work harder.
● Electrical Problems
Worn-out wiring, loose connections, or damaged capacitors can stop the motor.
● Blockages
Debris in the system can jam impellers.
● Overworking
A pump that is too small for the system may run at maximum output constantly, causing early failure.
Understanding the cause helps homeowners or installers decide whether repair or replacement is the better choice.
Benefits of Using Modern Circulation Pumps
Modern designs focus on efficiency, performance, and longevity. Some of the advantages include:
Up to 80% lower electricity consumption compared to old pumps
Automatic speed regulation
Quieter operation
Better protection against pump overheating
Improved compatibility with modern boilers
Longer service life due to improved motor technology
These improvements make modern pumps a cost-effective upgrade for older systems.
Practical Tips Before Buying a Circulation Pump
Here are some reliable, neutral tips to help any buyer choose the right pump:
Check the pump’s technical data sheet.
Match pump specs with your heating or plumbing layout.
Avoid choosing a high-power pump without calculations.
Consider future maintenance access during installation.
Ensure proper system flushing to avoid debris damage.
Look for general-purpose models from trusted manufacturers.
A little preparation prevents costly mistakes and ensures that the pump operates efficiently.
Conclusion
Circulation pumps may be small, but they play a major role in heating, cooling, and hot-water systems. Choosing the right pump improves comfort, reduces energy consumption, and protects the system from long-term wear. By understanding how these pumps work and what features matter, homeowners and professionals can make informed decisions without relying solely on marketing claims. Brands like BritTherm and resources such as www.brittherm.co.uk offer technical details that help buyers compare models, but the final choice should always depend on system requirements rather than promotion. This balanced approach ensures effective performance and reliable operation for years to come.




